200以上 yield stress vs yield strength 313390-What is the difference between yield stress and yield strength
Aluminium 6061T6 mechanical properties are listed in the following tables including yield strength (yield stress), ultimate tensile strength, shear strength, modulus of elasticity, young's modulus, etc Aluminum 6061 Mechanical Properties, Part1 Aluminum Alloy and TemperThe yield strength or yield stress is a material property and is the stress corresponding to the yield point at which the material begins to deform plastically The yield strength is often used to determine the maximum allowable load in a mechanical component, since it represents the upper limit to forces that can be applied without producingAluminium 6061T6 mechanical properties are listed in the following tables including yield strength (yield stress), ultimate tensile strength, shear strength, modulus of elasticity, young's modulus, etc Aluminum 6061 Mechanical Properties, Part1 Aluminum Alloy and Temper

Yield Point Instron
What is the difference between yield stress and yield strength
What is the difference between yield stress and yield strength-The stress value, in pounds per square inch, is the yield strength It is indicated in Figure 5 as Point 3 This method of plotting is done for the purpose of subtracting the elastic strain from the total strain, leaving the predetermined "permanent offset" as a remainderBut it may be that in the stressstrain community the yield strength is the more common expression for that point of the stressstrain curves due to the fact that it is a special characteristic



Yield Strength Graph Dubai Khalifa
Yield strength or yield stress is the material property defined as the stress at which a material begins to deform plastically whereas yield point is the point where nonlinear (elastic plastic) deformation begins Prior to the yield point, the material will deform elastically and will return to its original shape when the applied stress isFig 4 Their data for yield stress (YS), ultimate tensile strength (UTS), elongation to failure and grain size are summarized in Table 1 The UTS and YS increase with an increase in the number of pressings The ultimate tensile strength (UTS) and yield strength (YS) of the 4 pass ECAPed sample were found to be 577 MPa and 513 MPaYield strength or yield stress is the material property defined as the stress at which a material begins to deform plastically whereas yield point is the point where nonlinear (elastic plastic) deformation begins
Stress Measuring Yield Stress Approximate yield stress measurements can be gained by plotting the shear stress values for a range of shear rates, fitting a curve to the data, and extrapolating through the stress axis The intersect on the stress axis gives us our yield stress (figure 2)Stress Measuring Yield Stress Approximate yield stress measurements can be gained by plotting the shear stress values for a range of shear rates, fitting a curve to the data, and extrapolating through the stress axis The intersect on the stress axis gives us our yield stress (figure 2)Stress Measuring Yield Stress Approximate yield stress measurements can be gained by plotting the shear stress values for a range of shear rates, fitting a curve to the data, and extrapolating through the stress axis The intersect on the stress axis gives us our yield stress (figure 2)
In the case of FCC (Aluminum) and HCP(Zinc) metals no sharp yield points may be observed the yield strength is defined by the intersection of a line with the sigmastrain curve, which as a slopeThe yield strength is the transition point of stress where the deformation stops being elastic (nonpermanent) and becomes plastic (permanent) thereafter As for the 'practical limit', I learnt it as the proportional limit which is the point ofVon Mises stress is a yield criterion for metals Provided that the calculated stresses from your model are below the design yield strength (Fy/Omega for ASD or phi*Fy for lrfd), then the design is satisfactory for that limit state and your plates will not yield



Yield Strength Yield Point Stress Strain Curve



Tensile Testing Polymer Processing And Testing
Yield Strength vs Tensile Strength Tensile strength quantifies the force needed to pull a rope, wire, or a structural beam to the stage where it breaks Specifically, the tensile strength of a material is the maximum amount of tensile stress that it can withhold before failure occurs Yield strength, or the yield point, is describedYield strength is measured in N/m² or pascals The yield strength of a material is determined using a tensile test The results of the test are plotted on a stressstrain curve The stress at the point where the stressstrain curve deviates from proportionality is the yield strength of the materialThe yield strength is defined as the stress at which a predetermined amount of permanent deformation occurs When subjected to stress, a material undergoes deformation, yield strength describes the maximum amount of stress required to elastically deform the material in a given loading arrangement like tension and compression
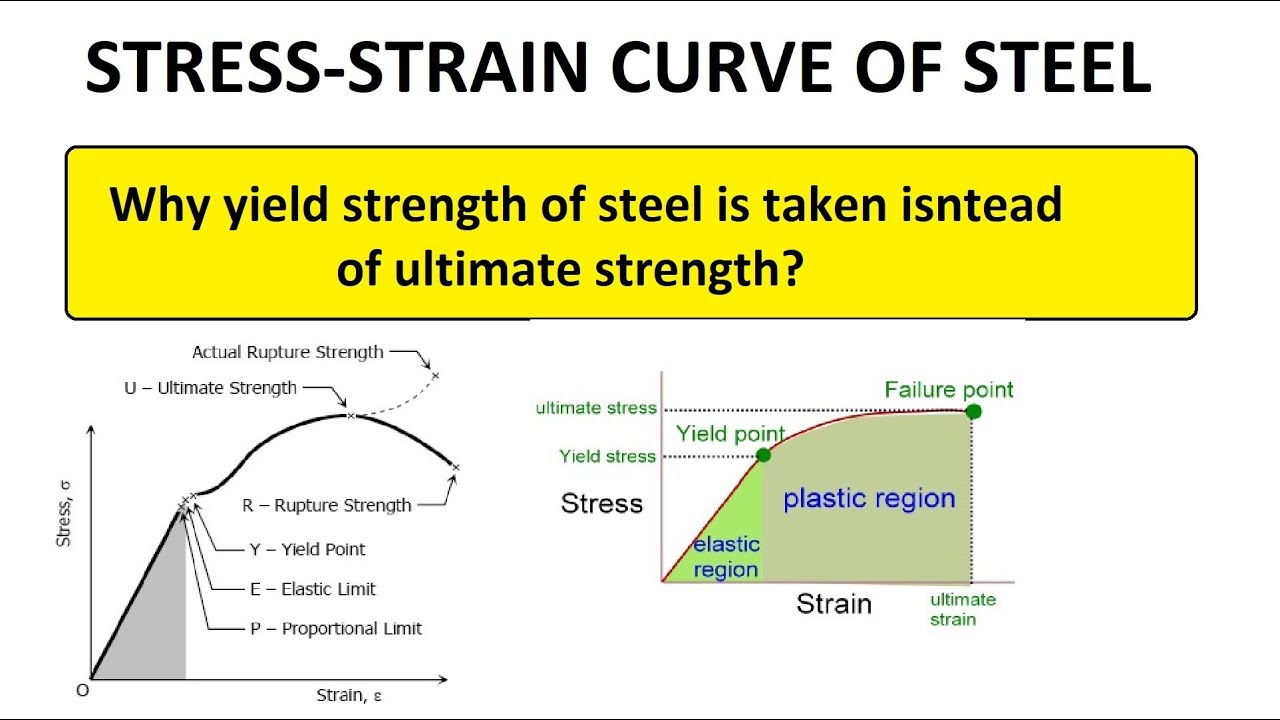


Hindi Stress Strain Curve For Steel Yield Strength Vs Ultimate Strength Youtube
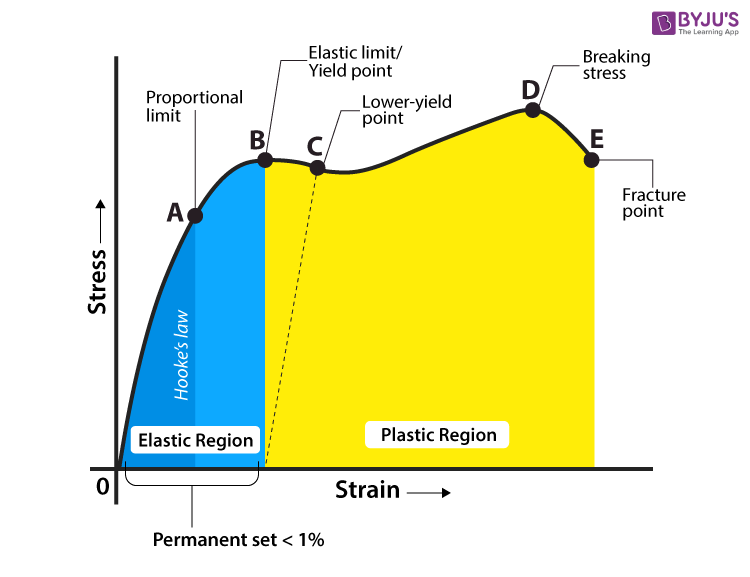


Yield Strength Definition Examples Stress Strain Graph Faqs
Strength is a critical factor in metal uses, for example, some applications require stronger aluminum parts, while some products need high steel hardness or yield strength of steel, this may determine the selection of CNC machining material or product design Here we collect the metal strength chart (tensile, yield strength, hardness, and density included) and mechanical properties chart ofFor metals, the allowable design stress is usually assumed to be 1/3 of the material's yield strength, or 1/4 of the tensile strength, but also depends upon the type of load being applied (ei seismic load, wind load, static load, fatigue load, etc)Dynamic and Static Yield Stress Static and Dynamic Yield Stress What's the difference and which should I use?


What Is Proof Load Of A Bolt And How Is It Different From Yield Strength Smartbolts


Difference Between Yield Strength And Tensile Strength
Yield Strength is the stress a material can withstand without permanent deformation or a point at which it will no longer return to its original dimensions (by 02% in length) Whereas, Tensile Strength is the maximum stress that a material can withstand while being stretched or pulled before failing or breakingFor metals, the allowable design stress is usually assumed to be 1/3 of the material's yield strength, or 1/4 of the tensile strength, but also depends upon the type of load being applied (ei seismic load, wind load, static load, fatigue load, etc)AISI 304 Stainless Steel (UNS S) AISI 304 stainless steel (UNS S) is the most widely used stainless steel, containing 10% Cr and 8105% Ni, and also known as 1 stainless steelType 304 is nonmagnetic under annealing conditions, but after cold working (such as stamping, stretching, bending, rolling), part of the austenite structure may be converted into martensite and
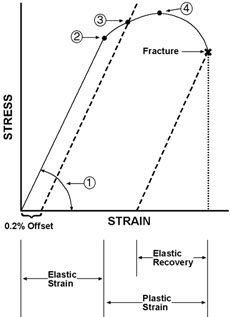


Industrial Design Guide Yield Strength


Http Web Mit Edu Dlizardo Www Uniaxialtestinglabreportv6 Pdf
A yield strength or yield point is the material property defined as the stress at which a material begins to deform plastically Prior to the yield point the material will deform elastically and will return to its original shape when the applied stress is removed Once the yield point is passed, some fraction of the deformation will beCurve Yield strength is assumed to be the maximum stress observed in each stressstrain diagram and the strain corresponding to the yield strength is the yield strain Stresscontrolled tensiontension fatigue tests were performed at 215 C The ratio of the minimum cyclic stress and the maximum cyclic stress, ie, the Rratio, was 01 AIn the case of FCC (Aluminum) and HCP(Zinc) metals no sharp yield points may be observed the yield strength is defined by the intersection of a line with the sigmastrain curve, which as a slope
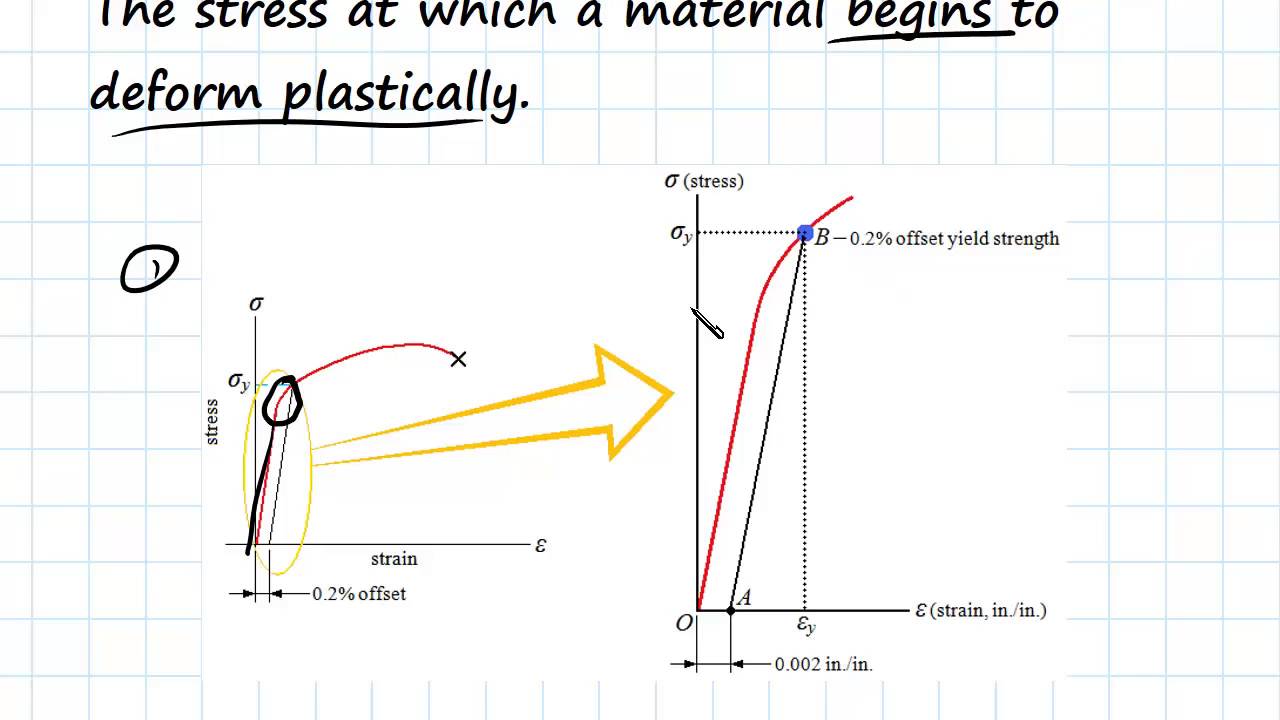


Yield And Tensile Strength Engineering Materials Youtube
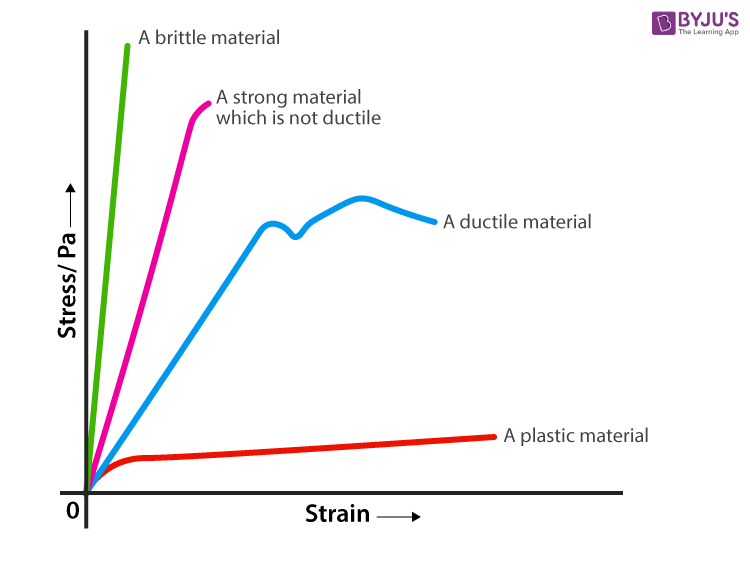


Yield Strength Definition Examples Stress Strain Graph Faqs
The magnitude of stress at which this transition occurs is known as the material's yield stress or strength The yield strength is a material constant that represents the limit of its elastic behavior Ductile materials like iron boast higher yield strength values than plastics, such as polyethyleneYield strength is used in materials that exhibit an elastic behavior It's the maximum tensile stress the material can handle before permanent deformation occurs Ultimate strength refers to the maximum stress before failure occurs Fracture strength is the value corresponding to the stress at which total failure occursFig 4 Their data for yield stress (YS), ultimate tensile strength (UTS), elongation to failure and grain size are summarized in Table 1 The UTS and YS increase with an increase in the number of pressings The ultimate tensile strength (UTS) and yield strength (YS) of the 4 pass ECAPed sample were found to be 577 MPa and 513 MPa



Stress Strain Properties 2 Matlab Cody Matlab Central
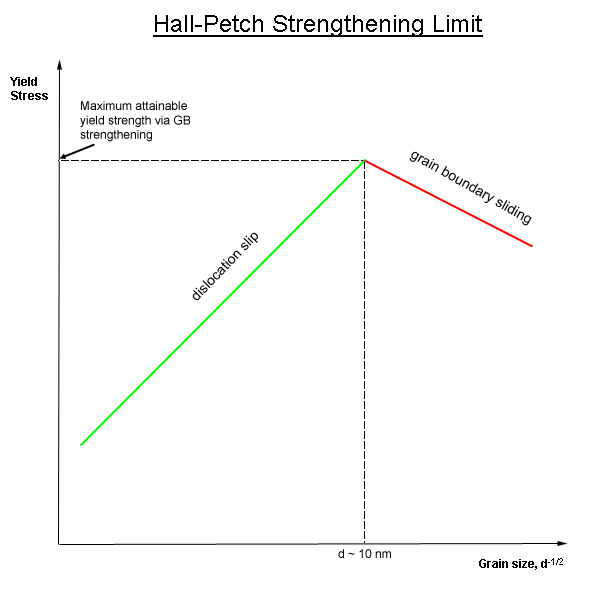


Grain Boundary Strengthening Wikipedia
Strength is a critical factor in metal uses, for example, some applications require stronger aluminum parts, while some products need high steel hardness or yield strength of steel, this may determine the selection of CNC machining material or product design Here we collect the metal strength chart (tensile, yield strength, hardness, and density included) and mechanical properties chart ofBoth formulae cap the column's maximum stress to its yield stress Both the RankineGordon and PerryRobertson formulae are means of determining the maximum average stress ($\sigma = P/A$) a given column can supportDue to the fact that short columns will collapse under compression rather than buckling, it's important that these equations cap the result to the material's compressive yield stressIe 06*UTS If you are looking at YS (Yield Strength) then SYS = 60% of YS;



Strength At Break Tensile



Engineering Fundamentals Refresh Strength Vs Stiffness Vs Hardness Fictiv
Compressive yield stress is measured in a manner identical to that done for tensile yield strength When testing metals, it is defined as the stress corresponding to 0002 in/in plastic strain For plastics, the compressive yield stress is measured at the point of permanent yield on the stressstrain curveYield strength is the stress which will cause a permanent deformation of 02% of the original dimension Ultimate strength The maximum stress a material can withstand Breaking strength The stress coordinate on the stressstrain curve at the point of rupture"The most commonly used method for obtaining a yield stress value is to shear the sample over a range of shear rates, plot the shear stress as a function of shear rate and fit a curve (various models are available) through the data points (see fig 1)
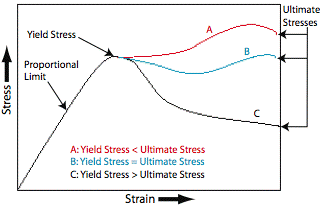


Design In Strength Of Materials Materials Links Resources Plastics
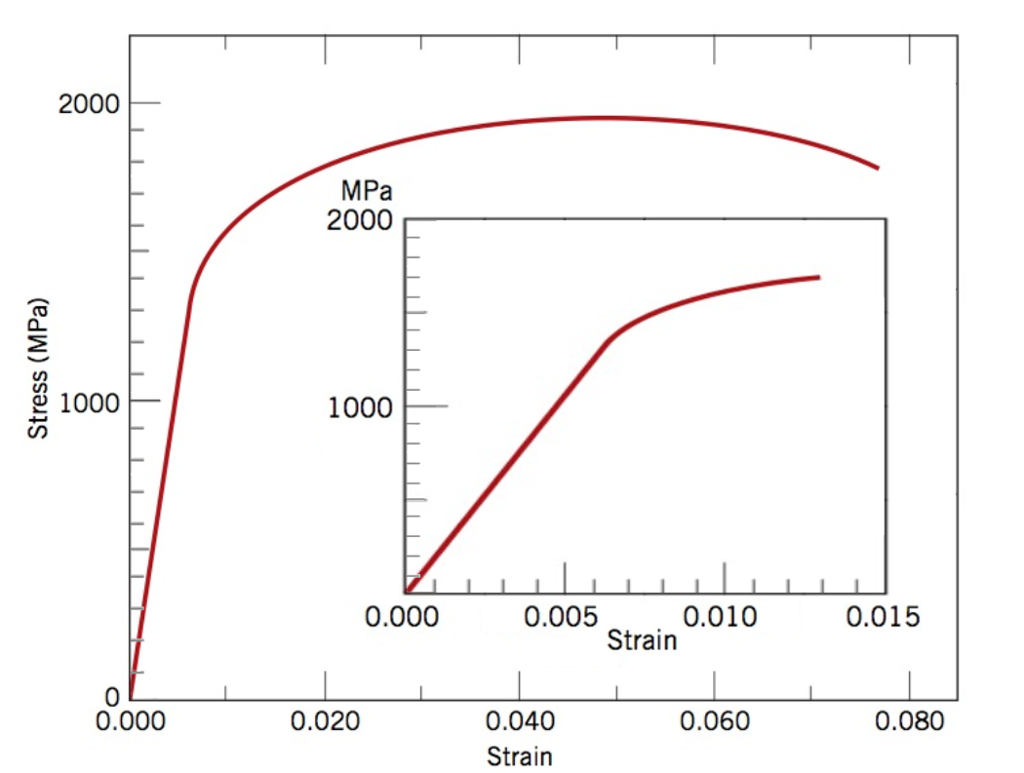


Solved A Using The 0 2 Strain 0 002 Strain Offset Met Chegg Com
Strength is a critical factor in metal uses, for example, some applications require stronger aluminum parts, while some products need high steel hardness or yield strength of steel, this may determine the selection of CNC machining material or product design Here we collect the metal strength chart (tensile, yield strength, hardness, and density included) and mechanical properties chart ofCompressive yield stress is measured in a manner identical to that done for tensile yield strength When testing metals, it is defined as the stress corresponding to 0002 in/in plastic strain For plastics, the compressive yield stress is measured at the point of permanent yield on the stressstrain curveThe stress value, in pounds per square inch, is the yield strength It is indicated in Figure 5 as Point 3 This method of plotting is done for the purpose of subtracting the elastic strain from the total strain, leaving the predetermined "permanent offset" as a remainder
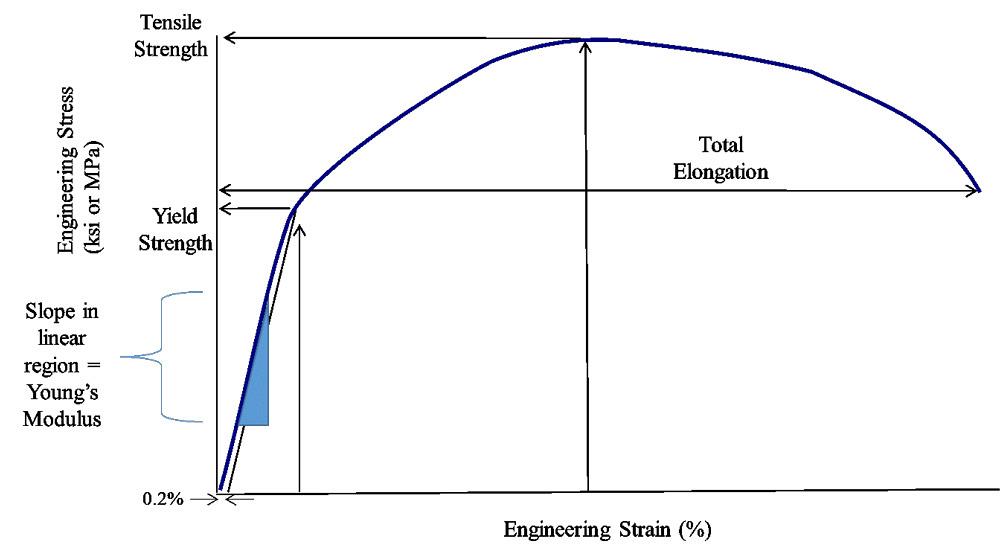


The Differences Between Stiffness And Strength In Metal



Changes In Yield Stress And Tensile Strength With Temperature For The Download Scientific Diagram
For example, aluminum has a yield strength of 14,000 pounds per square inch (or psi), copper has a yield strength of 10,000 psi, and steel, being an alloy of several different materials, has aTensile / yield strengths and ductilities for some of the plain carbon and low alloy steels are given in the following mechanical properties of steel chart Yield Strength, Tensile Strength and Ductility Values for Steels at Room TemperatureThe magnitude of stress at which this transition occurs is known as the material's yield stress or strength The yield strength is a material constant that represents the limit of its elastic behavior Ductile materials like iron boast higher yield strength values than plastics, such as polyethylene



Yield Strength Strength Mechanics Of Materials Engineers Edge



How To Find Yield Strength Quora
For mechanical engineering strength design applications it is accepted that shear strength is approximately 60% of tensile strength If UTS = 'x' (Ultimate Tensile Strength) This is the value usually reported in handbooks then USS = 60% of 'x';Aluminium 6061T6 mechanical properties are listed in the following tables including yield strength (yield stress), ultimate tensile strength, shear strength, modulus of elasticity, young's modulus, etc Aluminum 6061 Mechanical Properties, Part1 Aluminum Alloy and TemperYield strengths vary from 35 MPa for a lowstrength aluminum to greater than 1400 MPa for very highstrength steels Ultimate tensile strength The ultimate tensile strength is the maximum on the engineering stressstrain curve This corresponds to the maximum stress that can be sustained by a structure in tension Ultimate tensile strength is



Yield Strength Engineer Educators Com


Stress Strain Diagrams Showing Methods Of Yield Strength Determination Download Scientific Diagram
Yield strength is the stress which will cause a permanent deformation of 02% of the original dimension Ultimate strength The maximum stress a material can withstand Breaking strength The stress coordinate on the stressstrain curve at the point of rupture"Yield strength is the maximum stress that can be applied before it begins to change shape permanently This is an approximation of the elastic limit of the steel If stress is added to the metal but does not reach the yield point, it will return to its original shape after the stress is removedFig 4 Their data for yield stress (YS), ultimate tensile strength (UTS), elongation to failure and grain size are summarized in Table 1 The UTS and YS increase with an increase in the number of pressings The ultimate tensile strength (UTS) and yield strength (YS) of the 4 pass ECAPed sample were found to be 577 MPa and 513 MPa



Yield Strength Versus Ultimate Strength Physics Stack Exchange



Determining Tensile Test Offset Yield Strengths Using Extensometer Admet
Yield Strength Testing The stress a material can withstand without permanent deformation This is not a sharply defined point Yield strength is the stress which will cause a permanent deformation of 02% of the original dimension Point at which material exceeds the elastic limit and will not return to its origin shape or length if the stress is removedStrength yield strength (05%ext underload) yield strength (02%off set) yield strength (005% offset) el rockwell hardness vickens hard brinell hard shear strength fatigue strength* izod impact strength in % f ksi ksi ksi ksi % bc f30t 500 3000 ksi ksi ftlb mm c mpa mpa mpa mpa mpa mpa j m01 00 0 typ 68 67 30 21 115 134 22 00 00Tensile / yield strengths and ductilities for some of the plain carbon and low alloy steels are given in the following mechanical properties of steel chart Yield Strength, Tensile Strength and Ductility Values for Steels at Room Temperature
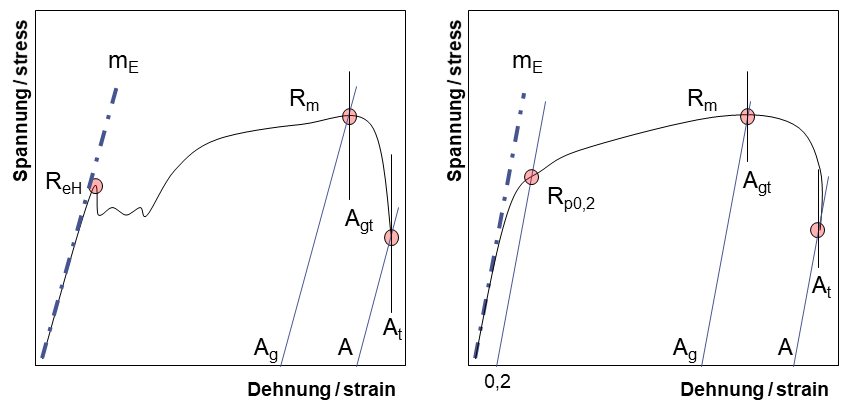


Yield Point Yield Point Ratio Offset Yield Zwickroell



Stress Strain Curve Wikipedia
Yield Strength Testing The stress a material can withstand without permanent deformation This is not a sharply defined point Yield strength is the stress which will cause a permanent deformation of 02% of the original dimension Point at which material exceeds the elastic limit and will not return to its origin shape or length if the stress is removedStress is a measure of the load applied to a sample relative to a cross sectional area of the sample Strength is a quantification of the samples ability to carry a load The terms "yield strength



Plotstressstrain File Exchange Matlab Central



What Is Yield Stress Definition Formula Video Lesson Transcript Study Com



Yield Strength Strength Mechanics Of Materials Engineers Edge



What S The Difference Between The Elastic Modulus And Kinetic Modulus Machine Design



Does Unloading Beyond Yield Point Also Affect Tensile Strength Engineering Stack Exchange
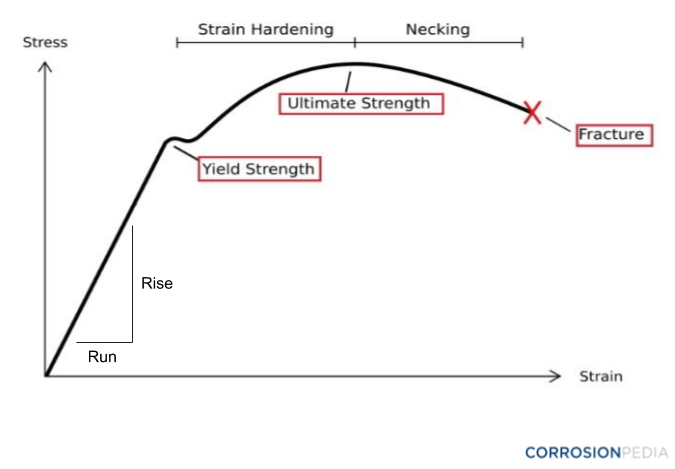


What Is A Proof Stress Definition From Corrosionpedia


Engarc L Offset Yield Method
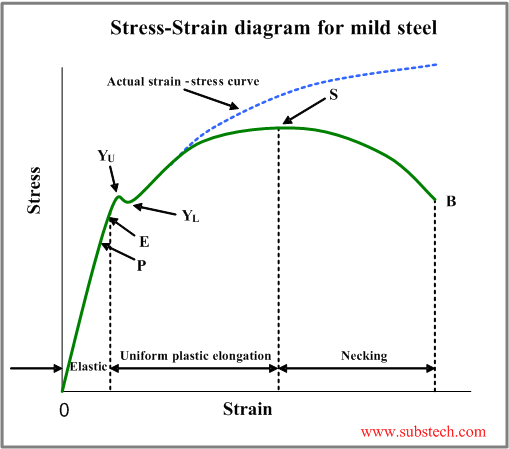


Tensile Test And Stress Strain Diagram Substech



What Is Yield Stress Definition Formula Video Lesson Transcript Study Com
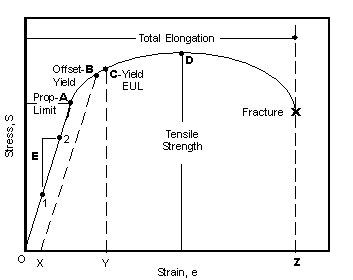


Astm E8 Measuring The Tensile Strength Of Metals



What Is The Von Mises Stress And The Yield Criterion


What Is The Basic Difference Between Yield Strength And Ultimate Strength For Any Elastic Material Quora



Engineering Stress Strain Curve Total Materia Article
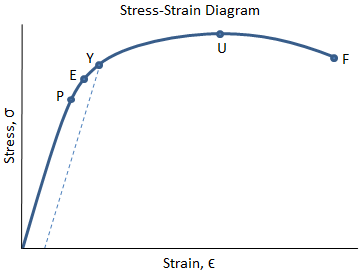


Mechanical Properties Of Materials Mechanicalc



Solved B Calculate The 0 2 Offset Yield Stress In Gpa Chegg Com



Sheet Metal Tension Testing Admet
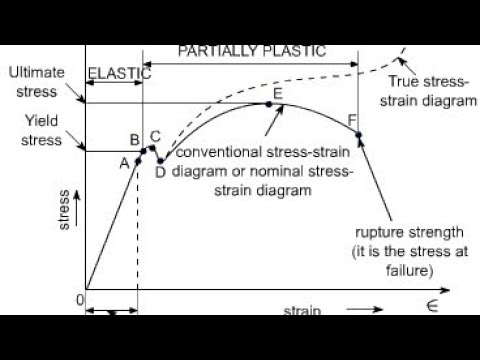


Stress Vs Strain Curve Yield Point Yield Strength Elastic Limit Neking Ultimate Tensile Youtube



Minimum Yield Strength An Overview Sciencedirect Topics



How To Measure Tensile Strength Elastic Modulus And Ductility Rolled Alloys Inc
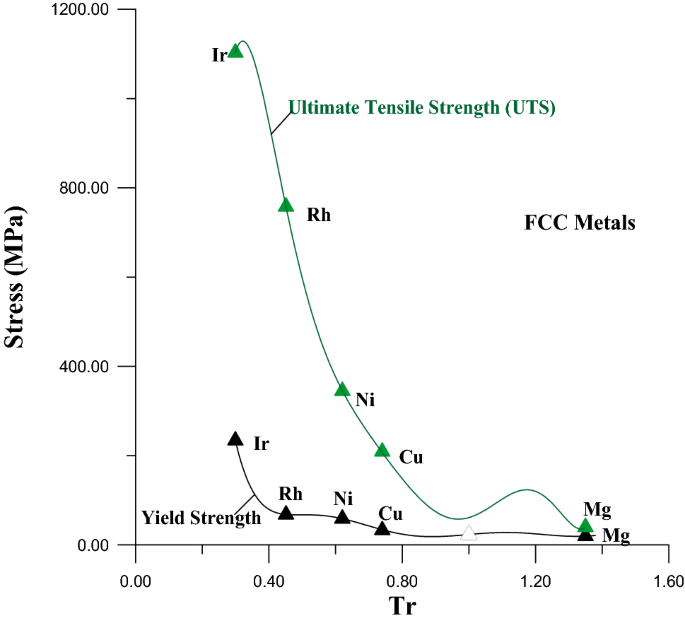


Estimation Of The Ultimate Tensile Strength And Yield Strength For The Pure Metals And Alloys By Using The Acoustic Wave Properties Scientific Reports
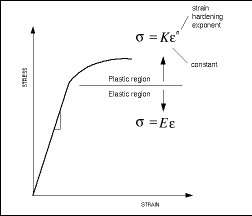


Importance Of Yield Strength Plastic Deformation To Civil Engineers
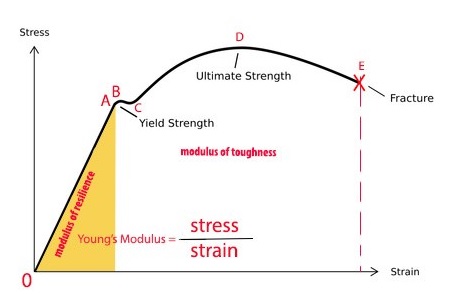


Exploring The Stress Strain Curve For Mild Steel The Chicago Curve


Q Tbn And9gcqpjlgtnnmrjaszc Eg Tgaba Nvxolrhabne8f9t4 Gzo3vax Usqp Cau



Thickness V S Yield Stress In This Graph We Are Changes The Thickness Download Scientific Diagram



Strain Ageing Of Steel Part One Total Materia Article



Yield Strength Of Steel



Definition Of Yield Point Download Scientific Diagram


Q Tbn And9gcs4 Kmbc0eevoesao31ukydn0fpdox Dykxkecqwqlk4eh7dc9j Usqp Cau



How Come The Yield Strength Is Greater Than Tensile Strength When Testing A Steel Specimen Quora



Yield Strength Graph Dubai Khalifa



What Is Proof Stress Civildigital


Q Tbn And9gcslkabgihai7oiceudovf Kl Msyzmkrbolgngnin4hsqzr2pre Usqp Cau



Yield Strength Metallurgy For Dummies
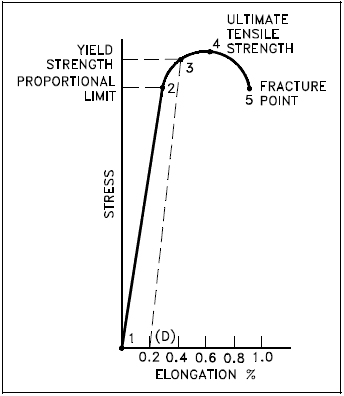


Properties Of Metals Engineering Library



Yield Strength Yield Point Stress Strain Curve



What Is The Relation Between Tensile Strength And Young S Modulus Of A Material
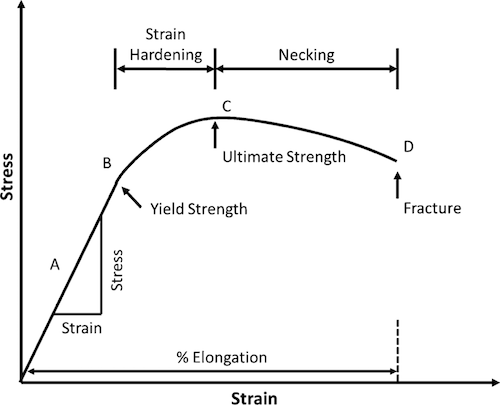


Cee 3710 Strength Versus Stiffness
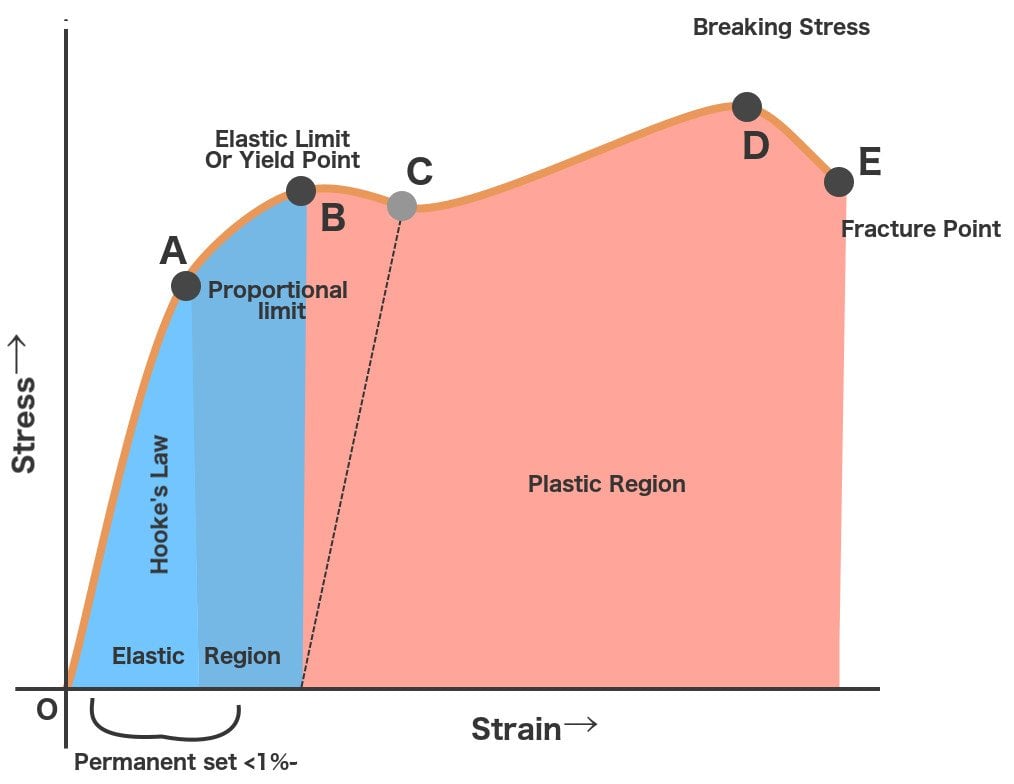


Yield Strength Defintion Examples And A Simplified Explanation



Stress Strain Curve An Overview Sciencedirect Topics



What Is The Difference Between 0 2 Yield Stress And Yield Stress In Aluminum Quora



Shear Yield Strength An Overview Sciencedirect Topics


What Is The Difference Between Tensile And Yield Strength Quora
.jpg)


Yield Stress Calculation Methods


Jenkins And Khanna Mechanics Materials Design Virtual Lab Tension Test



Tensile Strength Of Steel Vs Yield Strength Of Steel Clifton Steel
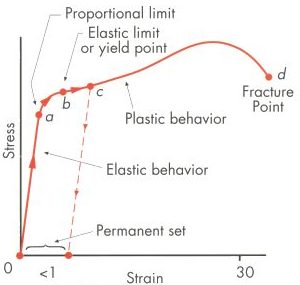


Importance Of Yield Strength Plastic Deformation To Civil Engineers



Yield Stress Vs Critical Load Stress Engineering Stack Exchange
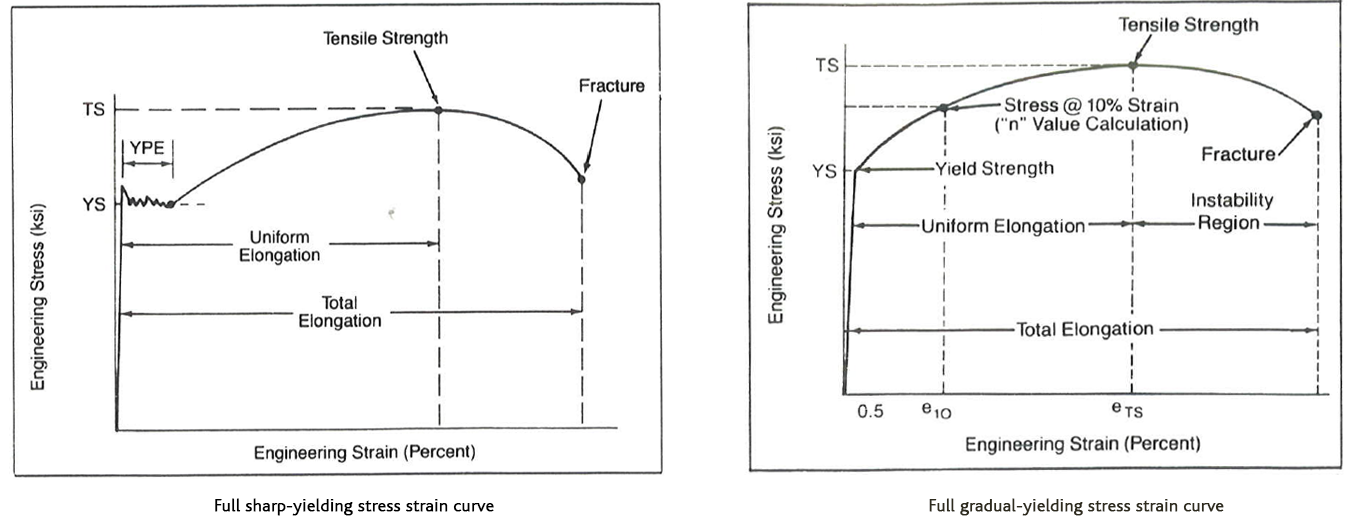


Tech Matters



Yield Point Instron


Tensile Strength Soft Matter



Stress And Strain Mechanical Properties Of Materials
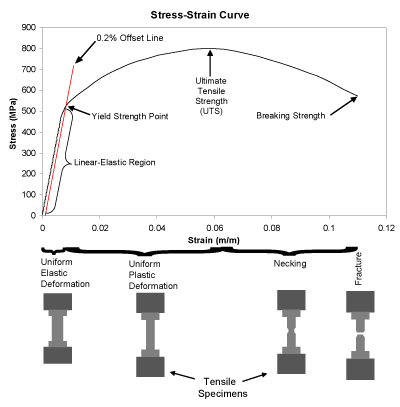


Nondestructive Evaluation Physics Materials



Yield Strength



Stress Strain Curve Wikipedia


What Is Yield In Materials Yield Stress Yield Strength And Yield Point Materials Science Engineering



Tensile Strength And Elongation At Yield Astm D638


Www Usna Edu Naoe Files Documents Courses En380 Course Notes Ch10 Deformation Pdf



Yield Engineering Wikipedia


1
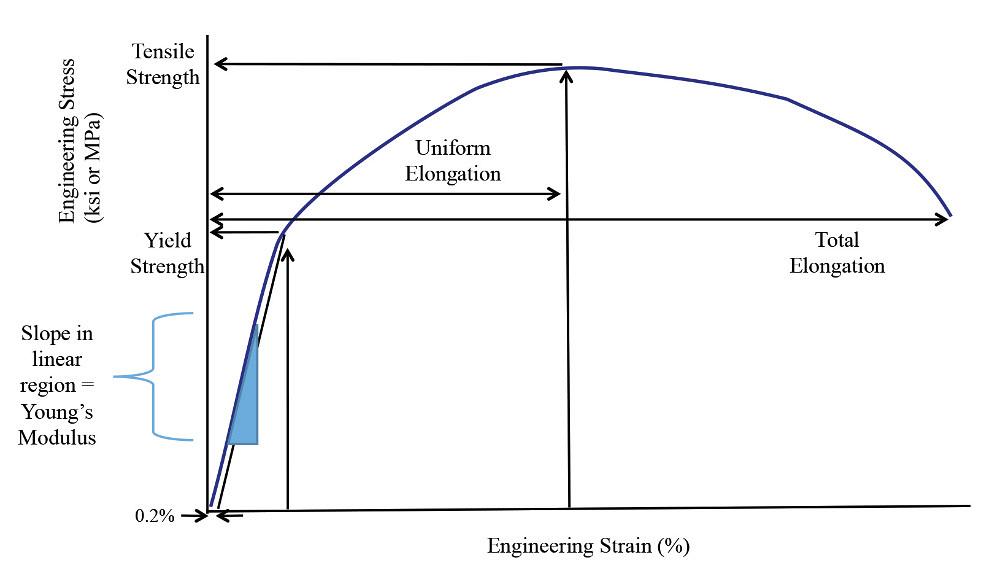


Getting To Know More About The Metal You Are Forming
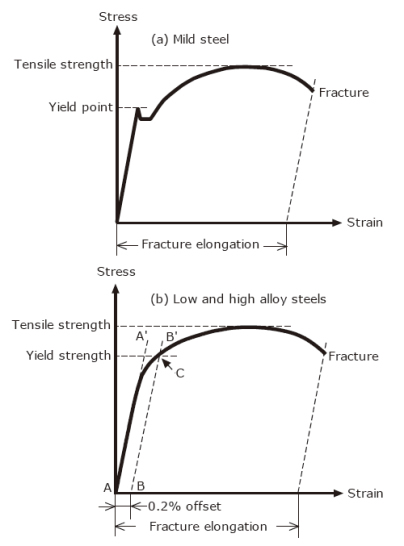


The Abc S Of Arc Welding Education Center Kobelco Kobe Steel Ltd
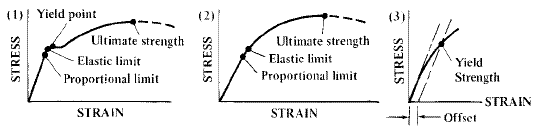


Strength Of Materials Basics And Equations Mechanics Of Materials Engineers Edge



Strength At Break Tensile



Yield Point An Overview Sciencedirect Topics



Fastener Ultimate Tensile Strength Vs Yield Strength Which Is More Important Extreme Bolt



Allowable Stress In Asme Viii 1 3 Api 650 Api 653 Amarine



Gel Strength Sigma Quadrant Drilling Engineering Books
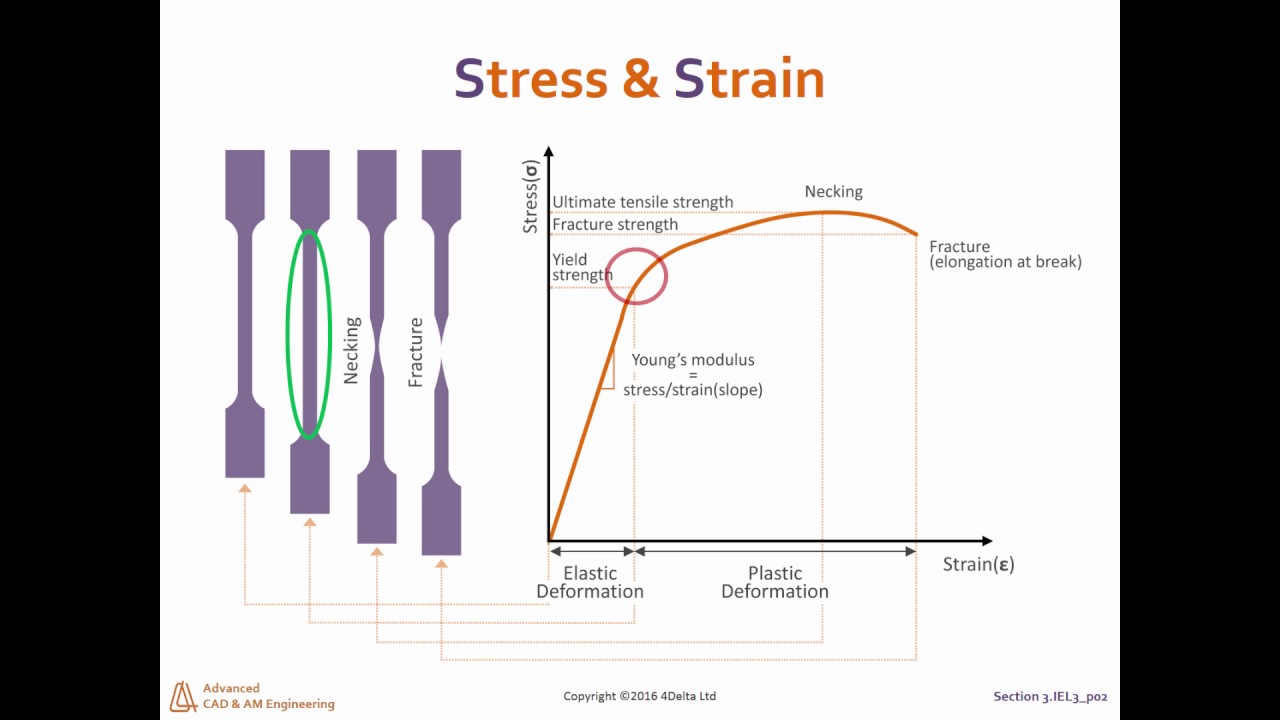


Yield Stress Yield Strenght Youtube


Stress Strain Behavior Of Polymers



Casing Design Theory And Practice Material Properties Definition Drilling Manual



Yield Stress Of A Material Simple Explanation Civildigital


Stress Versus Strain



Motion Design 101 Stress Strain Curves Machine Design



Hooke S Law And Stress Strain Curve Analysis Videos And Examples



Isbt212 04 3 Stress And Strain Proportional Limit And Yield Strength Youtube


What Is Yield In Materials Yield Stress Yield Strength And Yield Point Materials Science Engineering



Engineering Fundamentals Refresh Strength Vs Stiffness Vs Hardness Fictiv



What Is The Difference Between Upper Yield Point And Lower Yield Point Of A Stress Strain Curve For Mild Steel Quora


コメント
コメントを投稿